Dakota Audio » How It Works »
How it Works
When multiple sound waves arrive at random times, some waves cancel, producing a sound wave that is less than the sum of the incoming waves.
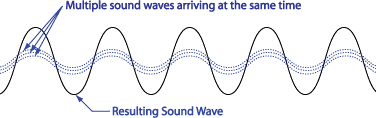
If two or more sound waves arrive at the same place at the same time, they add and produce a sound wave that is the sum of all of the incoming sound waves.

If several speakers are mounted equal distance from the listener, the sound from each of the speakers arrives at the listener's ears at the same time. The resulting sound is considerably louder than the sound from each individual speaker.

While it wouldn't be practical to mount the speakers in a spherical array, we can achieve the same results by delaying the launch time from the speakers.
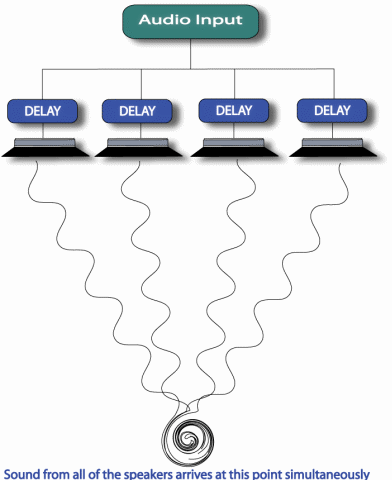
A further advantage of our technology is the flexibility that it allows. By changing the delay time, we can move the distance to the focal point, move the focal point sideways, or even change the size and shape of the focal area.